Where does the NMPA fit in with other HQIP-funded projects, such as the National Neonatal Audit Programme (NNAP) and MBRRACE-UK?
The NMPA works closely with both NNAP and MBRRACE, who are represented on our Clinical Reference Group.
NNAP uses the Neonatal Research Database, derived by the Neonatal Data Analysis Unit at Imperial College from the BadgerNet system which is used to record care of babies admitted to almost all neonatal units in the UK. From this, it establishes key measures of neonatal care in the UK. We are linking the NMPA dataset with the same neonatal dataset to find out more about what factors in pregnancy or during birth might cause babies to need neonatal care.
MBRRACE uses a different methodology; instead of using routinely collected data, clinicians submit detailed information directly about cases meeting the MBRRACE eligibility criteria. For example, if a mother dies in the UK, the clinicians looking after her make a phone call to the MBRRACE team, and subsequently follow a case reporting process. This is an excellent way of looking at relatively rare events in detail. The NMPA looks instead at routinely collected data collected about every birth and is thus able to report on more common events, such as induction of labour, for which a case reporting process would be impractical.
NMPA Methods
How are the data collected?
-
Clinical audit
It is not necessary for the maternity services to collect any additional data specifically for the clinical audit as we make use of data which are already collected routinely. The data used for each country are detailed below, and you can find further information in the NMPA data flow diagram.
- For England, data for 2017/18 births onwards comes from the Maternity Services Data Set (MSDS), with the MSDS data supplied directly to the NMPA by NHS England. For 2015/16 and 2016/17, English trusts provided a data extract from their local maternity record system directly to the NMPA.
- For Wales, the Digital Health and Care Wales (DCHW) supplies the NMPA with data from the Maternity Indicators data set (MIds), linked to the Patient Episode Database for Wales (PEDW).
- For Scotland, the Public Health Scotland (PHS) provides data from the Scottish Birth Record (SBR) and Scottish Morbidity Record (SMR02) datasets.
-
Snapshot audits
Bespoke data collection has not been required for the topic-specific snapshot audits, which make extensive use of data linkage to combine existing data sources. The NMPA are exploring the use of bespoke data collection for future audits.
-
Organisational Survey
As part of the audit, organisational surveys of NHS Trusts and Health Boards were conducted in 2017 and 2019. The organisational surveys collect information on service delivery and the organisation of maternity care and contribute to a better understanding of the care provided.
How were the measures for the clinical audit selected?
The selection of measures was guided by a panel of clinical and academic experts, including obstetricians, midwives, statisticians and health service researchers, as well as the NMPA Women and Families Involvement Group and organisations representing maternity and neonatal service users.
Where can I get more detail about the measures?
Information about the exact definitions of the NMPA measures, and about the data sources, fields and codes used, can be found in the NMPA Measures Technical Specification.
What is case mix adjustment?
Case mix adjustment (or risk adjustment) is a statistical process to take into account the characteristics of the women a maternity service cares for, such parity and maternal age. This makes the results more comparable between different services. Despite this, differences can still remain if some conditions are not well recorded, due to other data quality issues, or due to differences in the care provided.
The majority of NMPA measures are adjusted for case mix; the NMPA Measures Technical Specification provides details on the case mix factors used for each measure.
Why was the 2017 clinical report revised and what has changed?
Following publication of the first clinical audit report in November 2017, it came to light that some sites were affected by a data quality issue which impacted on results for modes of birth, VBAC, labour induction and postpartum haemorrhage. This prompted further analysis and the publication of a revised report in March 2018, which can be found here. To address the data quality issue, the revision included redefinition of the affected measures to include all fetal presentations, as opposed to cephalic only. As a consequence, some previously included sites have been excluded on data quality grounds, while others could now be included. It also means that results for most sites included in the audit changed to some degree, as did national rates. All trusts and boards participating in the audit were given the opportunity to check their results. Further information can be found here.
Does the NMPA cover all of the UK?
Currently, the NMPA includes England, Scotland and Wales (Great Britain). Northern Ireland are not participating in the NMPA at present but the audit may expand its coverage in the future.
What further resources are available for participating maternity services?
For further technical documentation relating to the NMPA, please see our Resources for maternity service providers. If there are any other resources that would be helpful to make available on this website, please contact us.
How does the NMPA minimise impact on services? (Burden Reduction Strategy)
From the contract period which started in 2023, the NMPA state-of-the-nation reports and interactive results will continue to be derived from the sole use of routine data from centralised maternity systems, preventing any additional data burden to participants.
The NMPA has also made the decision to avoid bespoke data collection in additional outputs, following discussion with our governance groups (including our clinical reference group, and women and families involvement group).
Therefore all NMPA outputs will use routinely collected data, meaning that the audit does not add any additional data burden on Trusts and Boards.
In the event that any future snapshot audits or additional outputs require bespoke data collection, significant consideration will be given to the data burden this would create.
Additionally, the NMPA will ensure an online platform is available to review any data in a quick and accessible way, with results provided to trust/board/hospitals at least two weeks before publication. This process will allow providers the opportunity to review, check and contextualise their data before publication, but it does not require any direct action.
Using the NMPA results
How can I view the clinical results?
The clinical results can be viewed in several ways:
- View by site or trust/board, with spine charts. To understand more about spine charts click here.
- View by measure (at site, trust/board, region/LMS or country level), with funnel or scatter plots, or tables
- Interactive results tables covering all maternity services and all measures, which can be filtered to view those of interest (at site or trust/board level)
The full reports and summaries on the Reports page provide aggregated data at country and national (Great Britain) level.
How can I view the 2017 and 2019 organisational survey results?
The organisational survey results can be viewed in several ways:
- Overviews
- Summary of information by site or trust/board
- Maps of maternity units and neonatal units across England, Scotland and Wales
- Services and facilities available by country
- Detailed comparisons with charts or tables (at site, trust/board, region/LMS, neonatal network or country level)
- The full reports and summaries provide aggregated data at country and national (Great Britain) level.
How do I compare between services?
For the clinical results, you can select display of a single location or of all locations in table format; all locations are always displayed on the funnel and scatter plots. When you hover over a point, it tells you which location this is, and the result for this location. Underneath the results table or plot, there is also some contextual information about the selected location.
To compare a limited number of specific locations, use the Interactive results tables.
For the organisational results you can select either all, or up to four locations for display in tables and charts. Maps show all sites, and have pop-ups with site information.
Why can’t I find separate information about labour wards versus alongside midwifery units on the same site?
Currently, the datasets do not provide us with sufficient information to distinguish whether a birth happened in an obstetric unit or an alongside midwifery unit (when located together). Therefore for these units, data are presented at site level.
How should I interpret these results?
In order to gain a full understanding of a service, you should look at the whole pattern of their results and explore the relationships between the indicators, rather than focusing on individual results that may stand out as being high or low. Many of the indicators are inter-related (for example, a site with a higher caesarean section rate may have a lower instrumental birth rate) and as such it is important to consider all results together, rather than in isolation. The full reports discuss the variation seen in each group of measures.
How does a funnel plot work and what is normal variation?
Watch a short video introduction to funnel plots.
A funnel plot is a graphical method for comparing the
performance of organisations, which takes the size of each organisation into
account. This is important because the amount by which the result of an
individual service may vary from the national mean is influenced by random
fluctuations related to the number of births within the service. Some variation in results is expected in healthcare, even when differences between the services in terms of the characteristics of the women in their care are taken into account as much as possible (case mix adjustment). Funnel plots provide a way to represent this variation and indicate where this is within or outside of expected limits.
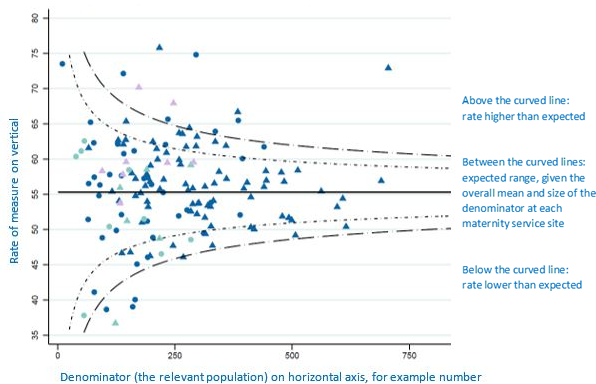
The straight central horizontal line is the overall mean. The values within the inner curved dotted lines are within the expected range, given this mean and the sample size of each site or trust/board. 1 in 20 values are expected to fall outside of the inner dotted lines by chance alone. 1 in 500 values are expected to fall outside of the outer lines by chance alone. Larger samples allow greater precision about the expected range.
If the result of a maternity service falls outside of the expected range, this does not necessarily mean that this is due to care quality; it could be (wholly or partly) due to data quality, remaining differences in case mix or organisational issues. However, it is a trigger to look into all the possible reasons for variation outside of the expected range.
The results for smoking cessation, skin to skin contact and babies given breast milk are displayed on scatter plots as data quality is not sufficient to allow comparison of performance between organisations with funnel plots.
What is a potential outlier?
A trust or board is classed as a potential outlier if it has a significantly higher than expected result for one of the NMPA outlier indicators. In the State Of The Nation Report based on 2023 data, these indicators were: blood loss of 1500ml or more, Apgar score of less than 7 at 5 minutes, and third and fourth degree tears. Having a high rate does not necessarily mean that the trust or board is providing ‘sub-standard’ care; there may be a number of contributing factors, for example better detection of tears or blood loss.
You can find out more about the process of detecting and following up outliers in our NMPA Outlier Policy document.
What is a spine chart?
Spine charts are useful to view results for measures in the context of other relevant measures at a selected site or trust/board, rather than in isolation.
Spine charts show the rates of all measures for the site or trust/board you have selected, and how these compare to the average of all sites or trusts/boards included in each measure. They also give an idea of the overall distributions of rates, and if the rates of the selected site or trust/board fall outside of the expected range. They are essentially slices of the funnel plot for each measure at the point of the site or trust/board you have selected.

How do I download tables and charts?
All tables and charts can be downloaded. Tables and spine charts have a download button, and funnel and scatter plots and bar charts have a blue striped icon in the bottom left corner for downloads in different formats. The names of the downloaded files can be quite long as they describe the content of the download. You may need to rename a file in order to save it, if the file path length on your local computer is exceeded.
Can women and birthing people use these results to choose which hospital to give birth in?
The NMPA results can be used by people using the maternity services to find out more about rates of events surrounding childbirth; the family gateway section of our website provides outputs specifically tailored for women and birthing people, and their families. The information that the NMPA produces is just one piece in the jigsaw to help you discuss and make choices about your maternity care. The family gateway provides links to other sources of information and resources, as well as a section providing tips on decision making and questions to ask during your appointments.
Information governance and data access (Fair Processing Notice)
Who uses details about me and my care for the NMPA?
The NMPA now receives all data pseudonymised from centralised organisations such as NHS England, Public Health Scotland, and Digital Health and Care Wales. This means we do not receive personal information such as your name, date of birth, address, postcode or NHS number).
The data utilised is routine data collected by units as part of their standard maternity care. The NMPA team members who use your information are employees at the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (this organisation is the Data Processor for the audit). NMPA team members are fully trained so they know how to keep your information secure. The contact details of the NMPA team are given on the Contact Us page.
The NMPA are currently exempt from the national data opt-out policy (applicable for data from England only). Find more information on the national opt-out here, including programmes which are currently exempt. The full NHS Data Protection Policy is here.
Who controls how the NMPA uses details about me and my care?
The Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership, who commission the NMPA, decide how the NMPA uses the information collected. The contact details of the Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership can be found on the GDPR Statement page of their website. This includes details of their Data Protection Officer.
Can I access the details the NMPA holds about me and my care?
For the audits based on births in 2015-2016, and 2016-2017, the NMPA received pseudonymised data which was handled by a small number of NMPA team members, using a secured server, before anonymised data were used by the rest of the team. NMPA team members are fully trained so they know how to keep your information secure. The contact details of the NMPA team are given on the Contact Us page.
If you gave birth between 1 April 2014 and 31st March 2017, and you would like to request access to the information we hold about you please contact the Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership, our commissioners, who decide what information we can share. For a summary of what information we collect about women and babies, what we do with the information and why, please see the NMPA information leaflets for women.
What is the legal basis for the NMPA holding my data?
Under General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR) rules on confidentiality we have a lawful basis to hold information on women and their babies. The purpose of the audit is to provide information to NHS maternity care providers to help them improve the quality of care women and their babies receive during pregnancy and childbirth. These uses are classified as justifiable purposes for using personal information (or a legitimate interest, GDPR Article 6(1)(e) and 9 (2) (i)).
The NMPA is allowed to handle data on pregnancies and births to audit NHS services without the informed consent of each woman and baby covered by the audit (Section 251 of the National Health Service Act 2006 – Control of Patient Information). For a copy of our Section 251 approval letter, see our Resources page.
National Data Opt Out exemption - England only
The NMPA submitted an application to the Confidentiality Advisory Group (CAG) to request an exemption to the National Data Opt Out. This request asked that the NMPA continues to have access to the pseudonymised data from all women and birthing people and their babies. As part of this application, the NMPA also included the views of women and birthing people whose data would form part of the audit.
The CAG recognised that for the NMPA, not receiving individual data from women and birthing people who have opted out of sharing their data would mean that the audit’s results would not be reflective of national maternity practice, raising concerns about NMPA data relating to quality of care, safety and introduction of bias. Given recent reports on standards of maternity care, the CAG recognised the importance of maintaining high quality data in this national audit. For these reasons, the NMPA was granted an exemption from the National Data Opt-out, meaning the data from all women and birthing people who give birth in England and Wales, and their babies will continue to be included in the audit. All English data is received by the NMPA with personal identifiers removed.
HRA CAG approval does not apply in Scotland.
How does the NMPA keep information secure?
The NMPA team make sure that information we hold on women and their babies is kept confidential and secure. We have comprehensive procedures and assurances in place, for example:
• Everyone in the NMPA team is fully trained in keeping information confidential and secure. We take the training every year.
• We have information security and information governance policies in place, which are regularly reviewed.
• We have done an official assessment of how well we are doing at keeping information secure (a Data Protection Impact Assessment, or DPIA).
• When we use birth and death registration information and information about your hospital appointments or stays, we are covered by Section 42(4) of the Statistics and Registration Service Act (2007) as amended by section 287 of the Health and Social Care Act (2012), which says that we can use this information to help NHS units provide and improve their services.
• We store all NMPA data in a secure server which is accessed by only named members of the NMPA team.
• We will securely destroy all information we hold after an agreed period with data providers after our contract for the audit ends. The reason for keeping the information after the contract is so that we can respond to enquiries about publications, for example from hospitals who want to investigate their results further.
How can I request access to NMPA data for secondary use?
If you would like to request access to data from the NMPA that isn’t available on our website, for purposes of quality improvement, including research, service evaluation and audit, please visit the Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership Data Access Request Group (HQIP DARG) website for more information. The Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership are our commissioners, who decide what information we can share. For certain information that we hold you will need extra permissions from the organisation who provided us with the data. We will let you know if this is the case.
Scottish inclusion in the NMPA
Why were Scotland not included in the clinical report based on births from 1st April 2018 to 31st March 2019?
Unlike previous NMPA clinical reports, the report covering 2018/19 births did not include data from Scottish NHS boards. The Scottish Government, on behalf of NHS Scotland and other stakeholders, worked with the Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership (HQIP) to try to identify a mutually agreeable legal basis that would support Scotland’s continued participation in the National Clinical Audit and Patient Outcomes Programme (NCAPOP – a collection of national quality improvement programmes commissioned by HQIP). That solution is now in place and Scotland is again participating in the NCAPOP, however that agreement was not in place in time for the preparation of this report, which means that maternity services in Scotland were not participants in the NMPA for the period of this report, but will be included in all subsequent NMPA clinical reports.
About the NMPA switch to the Maternity Services Data Set (MSDS) - England only
NMPA switch to using the MSDS
For data from 2017/18 onwards the NMPA has used the Maternity Services Data Set (MSDS) for English data. Prior to this the NMPA was sent data from each individual English trust. If you would like more information on the process and reasons behind this switch please click the link below:
NMPA MSDS Information
Questions not covered elsewhere
What happened to the Rapid Quarterly Reporting that used to be available on the NMPA website?
The NMPA is no longer commissioned to produce Rapid Quarterly Reporting Results; instead we are focusing on producing high quality annual comparative outcomes, which allow for benchmarking against other services and national guidelines, alongside snapshot audits focused on specific topics. If you are looking for more current data about an individual maternity service, we recommend you review the Maternity Services dashboard produced by NHS England.
Why aren’t caesarean birth rates reported in your 2018/19 Clinical Report?
The NMPA has been asked by commissioners not to report caesarean birth rates. This is in part due to potential for misinterpretation, as highlighted by the independent report into maternity care at Shrewsbury and Telford NHS trust. The NMPA are exploring alternative means to understand and contextualise the use of caesarean sections within maternity care.